- WC/960-01/F, ICCF Diamond Jubilee 1st Chess 960 World Cup Final
- WC/960-02/F, 2nd Chess 960 World Cup Final
- WC/960-03/F, 3rd Chess 960 World Cup Final (in progress)
There are plenty of games there for further analysis, but how valuable are correspondence games for understanding chess960? Many years ago I touched on this topic in More on Computer Assistance (October 2010). Although they were already strong at that time, chess engines have made even more advances since then. What can we learn from them?
The following chart shows the essential portion of the crosstable for the '2nd Chess 960 World Cup Final', which finished last year. For the full table, see the link above.
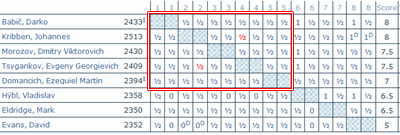
WC/960-02/F
The rectangle in red shows that the top five players drew all of their games with each other. (The '1/2-1/2' result in red was the last game to finish and has nothing to do with the rectangle.) In other words, all of the points that determined the eventual winners were scored against the three bottom finishers.
This observation indicates that the top players used more advanced hardware (and perhaps software) than the others. Their engine setups are all calculating roughly the same variations, so it's difficult to get an advantage over each other. The other three used less advanced setups that couldn't keep up with the top players.
In other words, correspondence chess has evolved to the point where the players have little to add to the chess content of the games. Their role is to pursue a more powerful environment for their engines. What can be learned about chess960 from this?
 Seen on this blog in the Google Adsense space on the right navigation bar. The little triangle in the upper right corner of the image is for Google's AdChoices. The 'CHESS960 (FRC)' is the header for the list of recent comments. (The usual widget in the space, 'RESOURCES', was missing that day.)
Seen on this blog in the Google Adsense space on the right navigation bar. The little triangle in the upper right corner of the image is for Google's AdChoices. The 'CHESS960 (FRC)' is the header for the list of recent comments. (The usual widget in the space, 'RESOURCES', was missing that day.)
